History
Morocco has a rich and complex history that dates back to the Phoenician and Berber civilizations. The country has seen the rise and fall of various empires, including the Roman, Arab, and French empires. The Berbers, who are the indigenous people of Morocco, established the first kingdom in the country around the 3rd century BCE (Adi, 2019).
In 711 CE, the Arab Conquest took place, which marked the start of the Arabization of Morocco. The country became part of the Arab empire and saw a rise in Islam, which became the dominant religion. During this time, Morocco experienced a cultural and economic flourishing, with the construction of mosques, palaces, and other significant buildings (Adi, 2019).
In the 16th century, Morocco became a major center of commerce and the center of the trans-Saharan trade route. The country prospered under the Saadian dynasty and the reign of Ahmed al-Mansur, who established close ties with the Ottoman Empire. In the late 17th century, the Alawite dynasty came to power, and the country saw a period of stability and prosperity (Adi, 2019).
In the 19th century, Morocco was colonized by the French and Spanish. The country became a protectorate of France, and the French introduced a number of reforms and modernization programs, including the construction of roads, railways, and schools. The period of French rule lasted until 1956, when Morocco gained independence (Adi, 2019).
Since independence, Morocco has undergone significant political and economic changes, including the reign of King Hassan II and the current reign of King Mohammed VI. The country has made significant progress in modernizing its infrastructure and has emerged as a major player in the African and Arab worlds (Adi, 2019).

Location
Morocco is a country located in North Africa and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It shares its borders with Western Sahara to the south, Algeria to the east, and Spain to the north (World Atlas, 2019).
The country is located on the northwestern coast of Africa and is considered to be a part of the Maghreb region along with Tunisia, Algeria, and Libya. Morocco is situated between the coordinates of 28° N and 34° N latitude and 7° W and 17° W longitude (National Geographic, 2020).
Climate
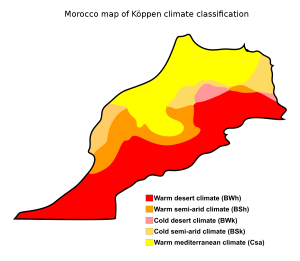
Morocco is influenced by a Mediterranean climate and a desert climate. The Mediterranean climate is characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate is found in coastal regions of Morocco, such as Casablanca, Rabat, and Tangier, where temperatures average between 68°F to 86°F in the summer and between 46°F to 60°F in the winter (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration [NOAA], 2021).
In contrast, the desert climate is characterized by hot, dry conditions, with temperatures often reaching over 100°F in the summer and dropping to freezing temperatures in the winter. This climate is found in the interior regions of Morocco, such as Marrakesh and the Sahara Desert, where temperatures average between 95°F to 104°F in the summer and between 50°F to 68°F in the winter (NOAA, 2021).
Morocco’s climate is also influenced by its location at the intersection of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, as well as its proximity to the Atlas Mountains. The country experiences a prevailing westerly wind that blows from the Atlantic Ocean, which can bring cool and moist air to coastal regions and create foggy conditions in the mountains (NOAA, 2021). The Atlas Mountains also act as a barrier, protecting coastal regions from the harsh desert conditions, and providing a more temperate climate for those regions.
In addition to the prevailing westerly winds, Morocco experiences occasional dust storms that can affect air quality and visibility, particularly in the desert regions. These dust storms are caused by strong winds that pick up sand and dust from the desert and carry it over long distances (NOAA, 2021).
Languages
Morocco is known for its rich cultural heritage and diversity. This is reflected in the languages spoken in Morocco, which include Arabic, Berber, French, and Spanish.
Arabic is the official language of Morocco and is used in official and governmental settings. According to the Moroccan National Institute of Statistics and Applied Economics (2015), 98% of the population speaks Moroccan Arabic, which is also known as Darija. This form of Arabic has been heavily influenced by Berber and French, and is considered to be a unique dialect in the Arab world.
Berber is another language that is widely spoken in Morocco. The Berbers are the indigenous people of Morocco and their language is known for its diversity and regional variations. There are three main Berber dialects in Morocco, Tamazight, Tashelhit, and Tarifit. According to the Moroccan National Institute of Statistics and Applied Economics (2015), Berber is spoken by more than 60% of the population, making it the second most widely spoken language in Morocco.
French is also a widely spoken language in Morocco, particularly in the cities and among the educated population. French was introduced to Morocco during the colonial period and is still used in education and the media. According to the Moroccan National Institute of Statistics and Applied Economics (2015), French is spoken by approximately 35% of the population.
Finally, Spanish is also spoken in Morocco due to its proximity to Spain. Spanish is particularly prevalent in the northern regions of the country, where there is a significant Spanish-speaking community.




