Gabon is a country located on the west coast of Central Africa, has a rich history that spans thousands of years. The region was inhabited by various ethnic groups, including the Bantu-speaking peoples, prior to European colonization. In the 15th century, Portuguese explorers arrived, followed by other European powers like the French and the Dutch, who established trading posts along the coast.
During the late 19th century, France claimed control over Gabon as part of its colonial empire. The country became a French colony in 1910. The colonial era brought significant changes to Gabon’s social, economic, and political landscape, including the exploitation of natural resources such as timber and rubber.
Gabon gained independence from France on August 17, 1960, with Léon M’ba becoming the country’s first president. The post-independence period was marked by efforts to establish a stable government and economy. Gabon’s leaders aimed to diversify the economy beyond resource extraction and develop sectors like oil production and tourism.
In 1967, M’ba was succeeded by his vice president, Albert-Bernard Bongo, who later changed his name to Omar Bongo. Bongo’s rule was characterized by authoritarian tendencies and a single-party political system. Despite this, Gabon managed to maintain relative stability compared to some of its neighbors in the region.
After Bongo’s death in 2009, his son, Ali Bongo Ondimba, assumed the presidency. His presidency has seen efforts to modernize the economy and promote social development, although concerns about transparency and democratic processes have persisted.

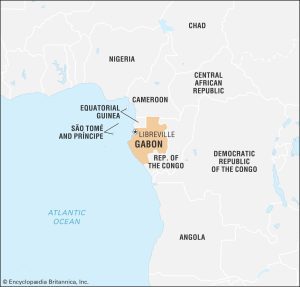
LOCATION OF GABON
Gabon is a country located on the west coast of Central Africa, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west (CIA World Factbook, 2021). Its geographical coordinates are approximately 0.4 degrees south latitude and 11.6 degrees east longitude (CIA World Factbook, 2021).
The country’s terrain is characterized by a combination of coastal plains, hills, and plateaus. The lush rainforests cover a significant portion of its land, hosting diverse flora and fauna (Encyclopedia Britannica, 2021). This geographical diversity has contributed to Gabon’s status as a biodiversity hotspot in the region (Encyclopedia Britannica, 2021).
In recent years, Gabon has been recognized for its efforts towards conservation and sustainable development, as it aims to protect its unique ecosystems and promote responsible resource management (UNDP, 2020). The country’s location along the equator also plays a role in its climate, characterized by a hot and humid tropical environment with distinct wet and dry seasons (Encyclopedia Britannica, 2021).
In conclusion, Gabon’s geographical location on the west coast of Central Africa, its rich diversity of landscapes and ecosystems, and its equatorial climate contribute to its unique identity and significance in the region.
CLIMATE OF GABON
Gabon, located in Central Africa, experiences a tropical climate with high temperatures and humidity throughout the year (Encyclopedia Britannica, 2021). The climate is influenced by its proximity to the equator and its position along the Atlantic Ocean. The country’s climate is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons, resulting from the movement of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) (National Geographic, 2020).
During the wet season, which typically occurs from October to April, Gabon receives heavy rainfall due to the southward migration of the ITCZ. This period is marked by frequent and intense precipitation, with some areas receiving more than 150 inches of rain annually (World Weather & Climate Information, n.d.). The humidity during this time remains high, contributing to lush vegetation and dense rainforests that cover a significant portion of the country (World Wildlife Fund, n.d.).
Conversely, the dry season lasts from May to September. During this period, the ITCZ moves northward, causing a reduction in rainfall. The dry season is characterized by lower humidity levels and less frequent rainfall, although some regions may still experience occasional showers (Climate-Data.org, n.d.). Temperatures remain relatively stable year-round, with average highs ranging between 80°F and 90°F (27°C – 32°C) and average lows ranging from 70°F to 75°F (21°C – 24°C) (BBC Weather, n.d.).
The oceanic influence from the Atlantic Ocean tempers extreme temperature fluctuations in Gabon. Coastal areas experience cooler temperatures compared to inland regions due to the maritime air influence (Encyclopedia of the Nations, n.d.). The warm ocean currents also contribute to the high humidity levels prevalent throughout the year.
In conclusion, Gabon’s climate is characterized by a tropical, equatorial climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The country’s proximity to the equator, as well as its location along the Atlantic Ocean, significantly influences its weather patterns. The wet season, occurring from October to April, brings heavy rainfall and high humidity, while the dry season, from May to September, is marked by lower humidity levels and reduced rainfall. The oceanic influence from the Atlantic Ocean plays a crucial role in shaping Gabon’s climate (The World Factbook, 2021).
