History
Qatar is a small country located in the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The country’s history dates back to the 18th century, where it was a desert land ruled by various tribes. During the 19th century, Qatar became a British protectorate, which helped it to establish trade relations with India and other parts of the world (Al-Horr & Saleh, 2018).
In the early 20th century, Qatar’s economy relied on pearl fishing and trade, but with the discovery of oil in the 1930s, the country’s economy rapidly developed. Qatar gained independence from Britain in 1971 and became an independent state. The country’s leadership has been passed down through the Al Thani family since the mid-19th century (Cordesman, 2019).
Since its independence, Qatar has gone through a series of developments that have transformed the country into a modern state. One of the most significant developments in recent times was the hosting of the 2022 FIFA World Cup, which has given the country global recognition (Cordesman, 2019).
However, the country has also faced several political and economic challenges. In 2017, several countries, including Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain, imposed a blockade on Qatar, which had significant economic and social consequences. Despite these challenges, Qatar has continued to pursue its vision of becoming a regional and global hub for trade, education, and innovation (Al-Horr & Saleh, 2018).
In conclusion, Qatar’s history is a story of transformation from a desert land to a modern state. The country has undergone significant economic and social changes, with the discovery of oil being a turning point. The leadership of the Al Thani family has played a crucial role in the country’s development, and the hosting of the 2022 FIFA World Cup has given the country global recognition. Qatar has also faced significant challenges, such as the 2017 blockade by neighboring countries, but the country continues to pursue its vision of becoming a regional and global hub for trade, education, and innovation.

Location
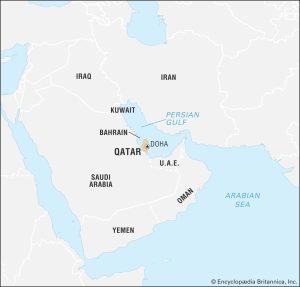
Qatar is a small Middle Eastern country located on the eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and the Persian Gulf to the north, east, and west (CIA World Factbook, 2021). The country covers a total area of 11,586 square kilometers, making it the 166th largest country in the world (CIA World Factbook, 2021). The capital city of Qatar is Doha, which is located on the central-eastern coast of the country (BBC News, 2021).
Qatar’s strategic location in the Persian Gulf has made it a significant player in the global economy. Its major industries include oil and natural gas production, petrochemicals, and fertilizers (CIA World Factbook, 2021). In recent years, Qatar has also made significant investments in industries such as tourism, education, and technology to diversify its economy (BBC News, 2021). Qatar has become a popular destination for tourists due to its modern cities, luxury shopping, and cultural attractions, such as the Museum of Islamic Art and the Katara Cultural Village (BBC News, 2021).
Qatar’s location has also made it a hub for international transportation and logistics. The country’s main airport, Hamad International Airport, is one of the busiest airports in the Middle East, connecting Qatar to destinations around the world (BBC News, 2021). Additionally, the country is home to one of the largest ports in the region, the Port of Doha, which handles a significant amount of the country’s imports and exports (CIA World Factbook, 2021).
In conclusion, Qatar is a small but strategically located country on the eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Its location has made it a significant player in the global economy, with major industries such as oil and natural gas production, petrochemicals, and logistics. Qatar has also made significant investments in diversifying its economy and becoming a destination for tourism and technology. Its location on the Persian Gulf has made it a hub for international transportation, with a major airport and port connecting it to destinations around the world.
Climate
The climate of Qatar is classified as arid with very hot summers and mild winters. According to the Köppen-Geiger climate classification, Qatar falls under the BWh category, which represents hot desert climate. The region is dominated by high pressure, which results in low precipitation and high temperatures throughout the year (Al-Kubaisi & Al-Sulaiti, 2016). The annual rainfall in Qatar ranges from 50-100 mm, which is significantly lower than the global average of 860 mm (World Weather Online, 2021).
The temperature in Qatar is relatively high, especially during the summer months. The average temperature in summer ranges from 36°C to 45°C, while in winter, the temperature drops to an average of 20°C to 25°C (Al-Kubaisi & Al-Sulaiti, 2016). However, the humidity levels in Qatar are low, which makes the heat more bearable. The summer heat is further intensified by the Shamal, a northwesterly wind that blows across the region during the summer months (Korntheuer, 2015).
The high temperatures in Qatar have a significant impact on the people, infrastructure, and economy. The extreme heat poses a health risk to people, especially those who work outdoors, and can lead to heat exhaustion and dehydration (Korntheuer, 2015). The heat can also cause damage to buildings, roads, and other infrastructure. The demand for air conditioning and cooling systems during the summer months increases, resulting in higher electricity consumption and higher greenhouse gas emissions (Korntheuer, 2015).
In conclusion, the climate of Qatar is arid, with high temperatures and low precipitation. The extreme heat during summer months is further intensified by the Shamal wind. The heat poses significant health risks to people and can cause damage to infrastructure, while the high demand for cooling systems during summer results in higher electricity consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.

Languages
Qatar, a small yet prominent Middle Eastern country, is home to a diverse group of people from different ethnicities and backgrounds. As a result, the country boasts a rich and diverse language landscape. In this article, we will explore the different languages spoken in Qatar.
The official language of Qatar is Arabic. Arabic is a Semitic language and is the fifth most widely spoken language in the world. It is the language of the Quran and is widely spoken across the Arab world. In Qatar, Arabic is used in all official communication, including government, education, and media. As a result, it is a vital language to learn for anyone wishing to integrate into Qatari society (Al-Ansari, 2018).
Apart from Arabic, English is widely spoken and understood in Qatar. English is a mandatory language in all schools in the country, and it is the language of instruction in many universities. Additionally, English is used in business, hospitality, and other industries, making it an essential language to learn for expatriates and tourists alike (Peng & Fang, 2020).
Hindi is another language that is widely spoken in Qatar. It is the fourth most widely spoken language in the world and is the mother tongue of many expatriates from India, Nepal, and other South Asian countries. It is used in everyday communication in shops, restaurants, and other public places (Gopakumar, 2019).
Finally, Urdu is also widely spoken in Qatar. Urdu is a language of South Asia and is the official language of Pakistan. It is spoken by many expatriates in Qatar from Pakistan and India. Urdu is used in various contexts, such as social gatherings and religious events, making it an important language to learn for those wishing to integrate into the Pakistani community in Qatar (Jaffar, 2018).
In conclusion, Qatar is a linguistically diverse country, with Arabic as the official language, English as the second language, and Hindi and Urdu widely spoken by the expatriate community. Learning these languages is crucial for anyone wishing to integrate into Qatari society.
