Belgium is a country located in Western Europe and is bordered by France, Germany, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands. It is a small country with a population of approximately 11 million people, making it one of the most densely populated countries in Europe. The country has a rich history and culture, and its location has made it a hub for trade and commerce, as well as a popular tourist destination.
History
Belgium is a country located in Western Europe that has a rich and complex history, dating back to prehistoric times. Archaeological evidence suggests that the region was inhabited by Neanderthal man as far back as 200,000 years ago (Leroy, 2017). The Celts, Romans, and Franks all left their mark on the region, with the Franks eventually establishing the Merovingian kingdom in the 5th century AD (Leroy, 2017).
In the 9th century, the region was incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire and, later, into the Burgundian Netherlands in the 15th century (Leroy, 2017). The Netherlands eventually became part of the Spanish Empire in the 16th century and was ruled by the Austrians in the 17th century before being occupied by the French in 1795 (Leroy, 2017).
In 1830, the southern provinces of the Netherlands declared independence and formed the Kingdom of Belgium, with Leopold I of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as its first king (Leroy, 2017). The country remained neutral in World War I but was occupied by Germany in World War II, with many of its citizens suffering from the German occupation and the country undergoing significant rebuilding efforts after the war (Leroy, 2017).

Belgium has since developed into a prosperous, modern nation and is a founding member of the European Union, NATO, and the United Nations, among other international organizations (Leroy, 2017).
Location
Belgium is a country located in Western Europe and is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. The country has a total area of 30,528 square kilometers and is home to over 11 million people (World Bank, 2021).
Belgium is situated on the Atlantic coastal plain and is divided into three main regions: the coastal plains in the northwest, the central rolling hills, and the Ardennes plateau in the southeast. The coastal plains are flat and low-lying and are home to many large cities such as Bruges and Ghent (Bruckers, 2017). The central rolling hills are characterized by rolling farmland and forests and are home to many smaller towns and villages. The Ardennes plateau is a mountainous region and is famous for its rugged and beautiful landscapes, making it a popular destination for outdoor activities such as hiking and camping (Belgium Tourism, 2021).
Brussels, the capital city of Belgium, is located in the central part of the country and is known for its beautiful architecture and rich cultural heritage. The city is home to many important institutions such as the European Union headquarters, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), and the Palace of Justice (Brussels Tourism, 2021).

Climate
Belgium has a temperate maritime climate, which is characterized by mild temperatures, moderate rainfall, and a lack of extreme weather conditions. According to the World Bank (2021), the average temperature in Belgium ranges from 4°C (39°F) in January to 17°C (63°F) in July.
The country experiences a moderate amount of precipitation throughout the year, with the wettest months typically being from October to January. In these months, precipitation is primarily in the form of rain, although snow is not uncommon in the winter months, especially in the higher elevations of the Ardennes region. According to the Belgian Meteorological Institute (2022), the average annual precipitation in Belgium is approximately 730 mm (28.7 inches), with the coastal areas typically receiving more rainfall than the inland regions.
Despite its temperate maritime climate, Belgium is exposed to various weather systems, including Atlantic low-pressure systems that bring significant amounts of rainfall, as well as continental high-pressure systems that bring sunny and dry weather. The country can also experience thunderstorms, particularly in the summer months.
Languages
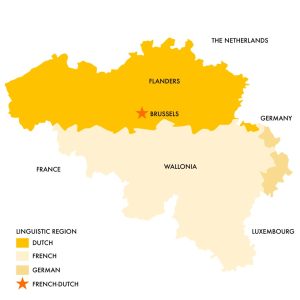
Belgium is a multilingual country located in Western Europe, and its official languages are Dutch, French, and German. According to the 2001 Belgian census, the majority of the population (58%) speaks Dutch, while French is spoken by 40% of the population, and 1% of the population speaks German (Statistics Belgium, 2021).
The use of these three languages in Belgium is heavily influenced by the country’s history and geography. Dutch is predominantly spoken in the northern region of Flanders, while French is primarily spoken in the southern region of Wallonia. German is mostly spoken in the eastern part of the country, particularly in the province of Liege (Statistics Belgium, 2021).
Despite the official recognition of these three languages, there are also several minority languages spoken in Belgium, including English, Arabic, Turkish, and Spanish (Statistics Belgium, 2021). These languages are primarily spoken by immigrants and their descendants who have settled in the country.
The linguistic landscape of Belgium is highly diverse, and the use of different languages reflects the country’s historical and geographical division. The official recognition of Dutch, French, and German, as well as the presence of minority languages, make Belgium a unique example of multilingualism in Europe.