History of Japan
Japan is an island country located in East Asia. The country has a rich and long history, dating back to thousands of years. Archaeological evidence suggests that the first human habitation in Japan occurred as early as 30,000 BC. The Jomon period, which lasted from 14,000 BC to 300 BC, is considered to be the earliest known culture in Japan.
In 710 AD, the Nara period began, and Buddhism was introduced from China. This was followed by the Heian period (794-1185), during which the capital was moved to Kyoto, and the development of a distinct Japanese culture took place (Ezra, 2009). During the Kamakura period (1185-1333), the samurai class rose to prominence, and the first Shogun was appointed.
In the 16th century, Japan entered a period of relative isolation, known as the Edo period, during which the country was ruled by the Tokugawa Shogunate. This isolation ended in the mid-19th century, when the country opened its doors to the rest of the world. In 1868, the Meiji restoration took place, and the Emperor was restored to power, leading to the modernization of Japan. (Ezra, 2009)
During World War II, Japan was defeated by the Allied Powers, and the country underwent major political and economic changes in the post-war period. Today, Japan is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of government, and is widely considered to be one of the most developed countries in the world.

Location
Japan is an island country located in East Asia, on the eastern coast of the Asian continent. It is made up of four main islands and several smaller islands, and is located in the Pacific Ocean, to the east of China, Korea, and Russia.
The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. Honshu is the largest of the four and is where the capital city of Tokyo is located.
Climate
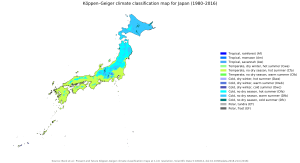
Japan has a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The country is located in the northern hemisphere and experiences warm summers and cold winters.
In the summer months (June to August), temperatures can reach up to 30°C (86°F) in some parts of Japan, while in the winter months (December to February), temperatures can drop to as low as -10°C (14°F) in some areas. The northern island of Hokkaido is known for particularly harsh winters (Ministry of the Environment, 2018).
Japan is also prone to heavy rain and typhoons during the rainy season, which typically occurs from June to July. In the autumn months (September to November), Japan is famous for its beautiful fall foliage, with leaves changing color and creating a stunning natural display.
Overall, Japan’s climate is relatively mild and comfortable, with temperatures ranging from 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F) for most of the year.
Languages
Japan has several languages spoken within its borders, including Japanese, Ryukyuan, Ainu, and others (Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, 2019)
Japanese:
Japanese is the official and most widely spoken language in Japan. It is a member of the Japonic language family and has a unique writing system consisting of three scripts: kanji, hiragana, and katakana. Japanese is used in all forms of communication, including education, government, and media.
Ryukyuan
Ryukyuan is a group of languages spoken by the Ryukyuans, who are indigenous to the Ryukyu Islands in southern Japan. Ryukyuan is considered a separate language from Japanese and has its own unique grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. It is recognized as a regional language by the Japanese government.
Ainu
Ainu is an indigenous language spoken by the Ainu people of Hokkaido, the northernmost island of Japan. Ainu is considered a minority language and has been in decline for many years. However, efforts have been made in recent years to preserve and revitalize the language.
Chinese
Chinese is widely spoken in Japan by the Chinese community, particularly in larger cities like Tokyo and Osaka. It is also studied in schools and universities as a foreign language.
English: English is widely spoken in Japan, particularly among young people and in international business settings. It is taught in schools and universities as a second language and is considered essential for international communication.
Korean
Korean is widely spoken in Japan by the Korean community, particularly in larger cities. It is also studied in schools and universities as a foreign language.